Workflow
Workflow
Our workflow is mostly based on the guidelines given at se-education.org/guides. This page points to the relevant parts of those guides and provide additional details specific to MarkBind.
To submit a PR, follow this guide, but note the following:
- You can start by looking through these issues marked good first issue. Don't do more than one of them though.
- As we squash the commits when merging a PR, there is no need to follow a strict commit organization or write elaborate commit messages for each commit.
- You can refer to the Design page to learn about the design and implementation of MarkBind.
The sections below has more information about various stages of submitting a PR.
Writing code
General tips
Use JavaScript ES6 features if possible for better performance, e.g. Promise instead of callback.
Do note our style guides.
Do set up your IDE debugger! We provide several sample configurations for WebStorm and VS Code.
Keeping your fork up to date
When new PRs are merged into the master branch, your master branch will be out of sync with the main repository. One way to update your branches to branch from the latest master is as follows:
Go to your fork on GitHub and click 'Sync fork' to update your remote
masterbranch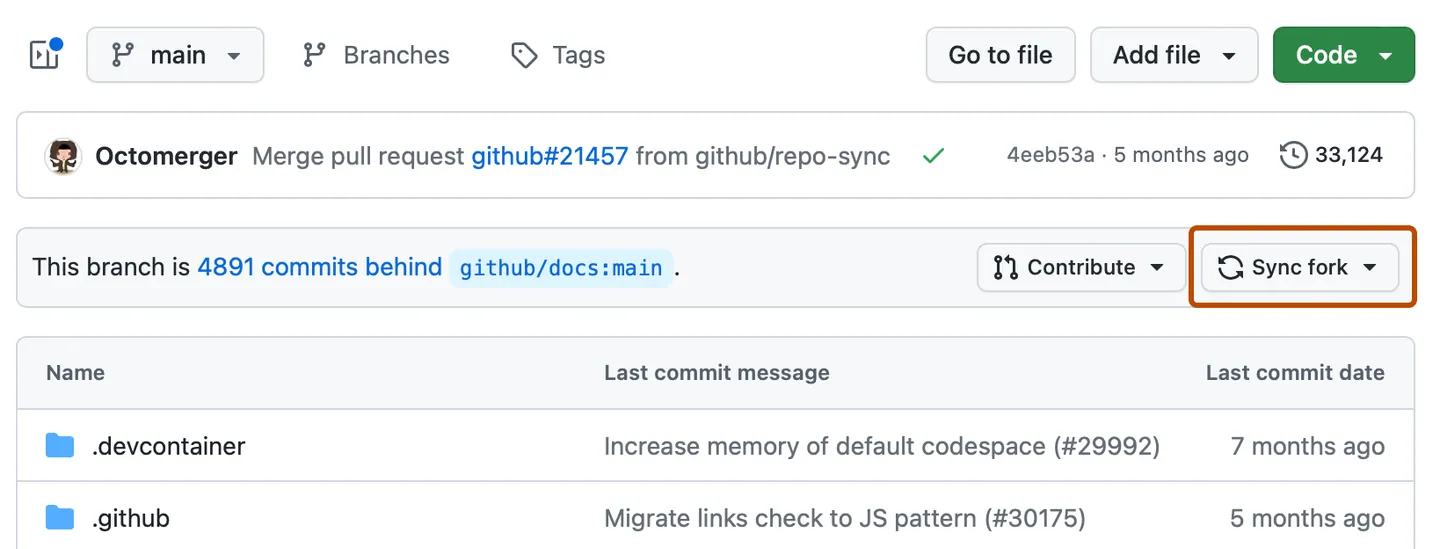
Checkout and sync your local
master(the name of your local branch that tracks the remotemaster) branch withgit checkout master && git pullCheckout your feature branch and rebase the branch with
git rebase masteror mergemasterinto the branch withgit merge masterFix any merge conflicts (if applicable)
You may want to use a tool like GitTown to speed up the process.
Editing backend features
Some of our backend code files in packages/core are written in TypeScript, and you will need to compile those into JavaScript for local execution with our command-line module packages/cli.
You can run npm run build:backend in the root directory to compile the files, but in some cases, it might be tedious to manually execute the command many times. We recommend you to either:
Run
npm run devin the root directory. (Recommended for TypeScript migration)This command starts the compiler's file watcher which will rebuild the relavant files when file changes are detected.
Configure your IDE to perform automatic compilation on file change/save. (Recommended for general development)
Refer to your IDE's guides to set this up. For instance, here are the guides for WebStorm and Visual Studio Code.
Editing frontend features
We update the frontend markbind.min.js and markbind.min.css bundles during release only, and not in pull requests.
Hence, if you need to view the latest frontend changes (relating to packages/core-web or packages/vue-components), you can either:
- Run
markbind serve -d(with any other applicable options). (recommended)
This adds the necessary webpack middlewares to the development server to compile the above bundles, and enables live and hot reloading for frontend source files. - Run
npm run build:webin the root directory, which builds the above bundles, then run your markbind-cli command of choice.
Testing
Our test script does the following:
- Lints the code (
.ts,.js,.vue) and stylesheets (.css) for any style errors using ESLint and StyleLint. - Runs unit tests for all packages with Jest.
- Builds the test sites whose directory names are listed in
packages/cli/test/functional/testSites.js. - For each test site, compares the HTML files generated with the HTML files in its
expecteddirectory.
To run the test script, use: npm run test
If you only want to run tests for one of the packages (packages/*), simply switch into the appropriate directory and use npm run test as well!
When running npm run test, you may see errors in the console. Some of these errors are expected as part of the test cases.
Check the test logs for messages like:
info: The following 2 errors are expected to be thrown during the test run:
info: 1: No such segment '#doesNotExist' in file
info: 2: Cyclic reference detected.
If an error is listed there, it's safe to ignore.
Updating and writing tests
If you're adding tests that are expected to log new errors to the console, make sure to update the corresponding info messages in the test logs. This ensures that expected errors are properly listed and avoids confusion during test runs.
Updating unit tests
Our unit tests perform fast, stable, and comprehensive checks on important behaviors of our classes and functions. Some existing tests can be found in the packages/cli/test/unit and packages/core/test/unit directory. Where appropriate, unit tests should be added/modified to account for any new/changed functionality.
Updating functional tests
Whether you are adding a new feature, updating existing features or fixing bugs, make sure to update the source test files (test sites, snapshots) to reflect the changes.
After which, you can update the with: npm run updatetest
You should always check that the generated output is correct before committing any changes to the test sites.
Note that some binary files such as images (e.g. inline-output.png) or fonts (e.g. material-icons-outlined.woff) could show up
as uncommitted changes due to the way they are generated. If you are not directly modifying those files in your PR, you should discard those changes and do not commit them.
Here are the steps to solve merge conflicts in expected test files:
- Ensure that your fork is synced with the upstream repository.
- Ensure that the master branch of your local repository is in sync with the master branch of your fork. Pull from the fork into your local repository as needed.
- Checkout from your master branch to your PR branch.
git checkout [BRANCH NAME]
- Merge your master branch into your PR branch.
git merge master
- Accept all changes to any merge conflicts in the generated expected test files.
- It does not matter which changes are accepted, as they will be overridden in the following step.
- Once your master branch has been successfully merged into your PR branch, run
npm run updatetestto generate the latest test files.
Adding test site content
When adding new features, you should also add new site content into an existing test site or create a new test site to demonstrate the new feature. This is to ensure that your feature can be tested by building that test site.
To add a page to an existing test site, for this example, to test_site:
Add a new test page, e.g.,
newTestPage.md, containing a demonstration of the new feature.Open the
site.jsoncorresponding to the test site, i.e.packages/cli/test/functional/test_site/site.jsonTo include the new page, i.e.
newTestPage.md, add it to thepagesarray.site.json"pages": [ { "src": "index.md", "title": "Hello World", "frontmatter": { "frontmatterOverrideProperty": "Overridden by frontmatter override", "globalAndFrontmatterOverrideProperty": "Overridden by frontmatter override" } }, ... { "src": "testLayouts.md", "title": "Hello World" }, {, "src": "newTestPage.md", "title": [some title you see fit] }, ...Update the tests using
npm run updatetest.
If creating a new test site instead, the directory name of the new test site should be added to packages/cli/test/functional/testSites.js file.
We do not commit the generated plantuml images in our test_site to avoid non-related file changes after npm run updatetest.
The existing list of images to be ignored is maintained in packages/cli/test/functional/testSites.js and .gitignore.
They should be updated accordingly if you are making changes to the plantuml content in our test_site.
Adding snapshot tests for components
When making changes to the Vue components in packages/vue-components, you should add new snapshot tests or adapt existing ones as appropriate.
Once you're done, be sure to run the updatetest script mentioned above!
Documenting
Adding Intra-Site Links to Documentation
In MarkBind, we use tags to differentiate between links in the developer guide referring to the user guide versus links in the user guide referring to the developer guide. Note that intra-site links within either guides need not have tags.
MarkBind's documentation currently has 3 tags:
environment--combinedfor deploying the User Guide and Developer Guide togetherenvironment--ugfor deployed User Guideenvironment--dgfor deployed Developer Guide
To ensure that correct links are created, use tags with the links to selectively filter the correct link to be rendered for the right environment. When both the User Guide and the Developer Guide are deployed together, they have access to the files from each other, allowing the relative link to work. However, when they are deployed individually, this is not the case. Using absolute links creates the same effect as the relative link without having to have access to the files from the other guide.
Developer Guide
LINK:
[Link Title](/userGuide/newPage.html)
REPLACED WITH:
<a tags="environment--combined" href="/userGuide/newPage.html">Link Title</a>
<a tags="environment--dg" href="https://markbind.org/userGuide/newPage.html">Link Title</a>
User Guide
LINK:
[Link Title](/devGuide/newPage.html)
REPLACED WITH:
<a tags="environment--combined" href="/devGuide/newPage.html">Link Title</a>
<a tags="environment--ug" href="https://markbind.org/devdocs/devGuide/newPage.html">Link Title</a>
Linting
We follow our style guides. Using a linter will help check and fix some of the code style errors in your code. It will save time for both you and your code reviewer. The linting tool we use is ESLint and StyleLint. Here is a gist with an explanation of the ESLint rules chosen in markbind-cli.
Before making a commit or pull request, you should lint your code by running the following commands from the root of your project:
- To lint a specific file:
eslint path/to/specificfile.js - To lint all files:
npm run lint
It is also possible to auto-fix some (not all) style errors, using npm run lintfix.
ESLint has integrations with popular editors. They offer features such as "fix errors on save", which will make development smoother.
Git hooks
We have three git hooks in our project. We use pre-commit to manage our git hooks.
The pre-commit scripts are located in ./pre-commit/pre-commit-scripts and the config is found in ./pre-commit-config.yaml.
To skip running the pre-commit hook or pre-push hook, you can use the --no-verify flag (e.g. git push --no-verify origin fork_branch).
post-checkout: When you checkout to another branch, this hook will run clean and build the backend.pre-commit: This hook will run clean, build the backend, and run lintfix on all the files.pre-push: This hook will run clean, build the backend, and run all the test cases.
Dependency management
As mentioned in the setting up page, MarkBind uses lerna to manage the dependencies of its various packages.
To add a dependency
Add your dependency into the appropriate package.json file inside packages/*. If this is a development dependency to be used across all packages (e.g. ESLint), add it the the root package.json.
Then, simply rerun the npm run setup command to update the package-lock.json files.
To delete a dependency
The safest way is to first remove the particular dependency entry from the package.json file of the respective directory. Then, run npm run setup in the root directory to clean up the local dependencies and update the package-lock.json file.
To update a dependency
First, follow the instruction to delete the dependency. Then, follow the instruction to add the latest dependency back. Also, when updating dependencies, ensure that it is updated in all packages using that dependency.
Dependency updates are not trivial, and can be the source of subtle bugs. You should always check the respective dependency changelogs before doing so!
Points for consideration
There are a few ways to incorporate external packages into MarkBind, each with its pros and cons. The following table shows some of the common trade-offs:
| Approach | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Installing |
|
|
| Forking |
|
|
| Patching |
|
|
As the choice is highly dependent on context and details of the implementation, below are some additional questions to ask before proceeding:
- Is the package actively maintained?
- How big is the package?
- How invasive are the proposed changes?
- Are there existing APIs/plugin system from the package (to modify default behaviors)?
Find out more about the key external libraries used in MarkBind from the project structure section. Also, the rationales behind most existing patches are documented in their respective files, read them (and their respective PRs/issues) for more context!
Updating PlantUML
PlantUML is a third-party library used by MarkBind to create UML diagrams. MarkBind runs the PlantUML JAR file found in packages/core/src/plugins/default when building the site to generate the diagrams.
To update PlantUML to a newer version:
- Download the JAR file from PlantUML's website.
- Rename the file to
plantuml.jar(if required), and replace the existing JAR file located inpackages/core/src/plugins/default. - Check the HTML pages that contain PlantUML diagrams, i.e.
/userGuide/components/imagesAndDiagrams.html.
Updating Bootstrap and Bootswatch
As Bootswatch is built on Bootstrap, ensure that the versions of both are in sync to avoid unexpected differences in styling behavior between default and other themes. Both are currently using version 5.1.3.
Using Skills
As a developer, you may use AI in your workflow to perform tasks. If a specific task is done repeatedly, you may leverage Skills to improve AI output and save time.
Skills are invoked whenever an agent detects a task to be relevant to one, though sometimes manual pointing may be necessary.
MarkBind houses several skills that you may find useful. See the Skills page for a full list and more information.